Tormach unveils a truly capable desktop CNC machine
The maker community is turning into a quickly-growing movement, as shown by the ever-expanding Maker Faires popping up worldwide. This last weekend was World Maker Faire in New York, where Tormach, a company known for making small, affordable CNC machine tools announced an even smaller, more personal mill, the PCNC 440.
Following in the footsteps of recent desktop CNC (computer numerical control) machines like Carvey and X-Carve, the PCNC 440 mill is designed to fit on benchtops, and lower the barrier of entry to real CNC. What’s different is that this machine is less like a router – it’s truly a CNC mill – allowing travel of 10 x 6.25 x 10 inches / 25.4 x 15.9 x 25.4 cm (X x Y x Z).
Real Machining
With an R8 spindle, a spindle speed of up to 10,000 RPM and quick-change tooling, Tormach has taken cues from its industrial brethren, but managed to make its machine more approachable. Like major industrial machines, both CAD (computer aided design) and CAM (computer aided manufacturing) software are needed to create a part on the PCNC 440. Being that these are often expensive and cumbersome to learn, Tormach has partnered with Autodesk to provide a free year-long seat to a commercial version of Fusion 360 (CAD/CAM) with the purchase of this machine.
Because the PCNC 440 requires traditional software workflows to start cutting parts – unlike other desktop-style CNCs and 3D printers that allow a drag-and-drop file workflow – to some, this may be where the 440 falls short of other maker-oriented cutting machines.
"CNC Machining still does not have a one button print function like many of the desktop 3D printers," Tormach’s product marketing manager Andy Grevstad explains. "The PCNC 440 is easily the most approachable CNC mill for beginners, but you’ll still need to invest some time to learn machining techniques and CAD/CAM programming skills. While it lacks the instant gratification of a 3D printer, it is a much more capable and rewarding technology in many aspects."
Also, like its bigger brothers in the industrial world, this machine can cut everything from wood and plastics to real metals like aluminum, steel and even titanium, with precision – although a bit slower. In comparison, one of the smallest industrial machines, the Haas MiniMill, uses a 7.5 HP spindle, compared to the PCNC 440’s ¾ HP spindle, but a MiniMill starts at US$34,995, while the 440 starts at just $4,950.
"[The PCNC 440] is more for small prototype work, inventors, educators, and specialty manufacturing," Grevstad says. "There is a need for CNC milling technology outside of traditional manufacturing environments and I think that the PCNC 440 fills that role."
Still for the Maker
What the machine lacks because of complexity, it gains in approachability. Tormach has developed PathPilot, the company’s machine control system which is rooted in the open-source Linux CNC project. This software reads any industry-standard G-code and also has some conversational programming for those that like to edit and tweak things on the fly.
While Tormach makes two other larger CNC mills (the PCNC 1100 and PCNC 770) and a CNC lathe, the PCNC 440 keeps the tinkering audience in mind. It weighs just 450 lb (204 kg), has a compact footprint of 42 x 36 inches / 106.7 x 91.4 cm (W x D), and runs on 115 VAC, single-phase power.
There's more on the way for the PCNC 440, too – Tormach plans to release a power drawbar, an automatic tool changer, and a 4th axis sometime in early 2016, making this thing a tiny, all-encompassing manufacturing center.
Currently, the PCNC 440 is available for pre-order only, due to ship in November. Grevstad is sure we will continue to see new advances in many facets of affordable digital tools for things like at-home manufacturing. "It’s an exciting time for makers and those that want to make things," he says.
Page Source : http://goo.gl/2wAJiw
website: www.subauae.com
Post By : Irfan Khan
Monday, October 26, 2015
Saturday, October 24, 2015
What is The Use of Cnc Machines
Computer Numerical Control
CNC (computer Numerical control) is a Method for controlling machinery with a computer, it can allow precise and repeatable control of over a larger number of axes then a human could directly control.
CNC machines usually work in one of two ways:
1.Removing material from stock-mills and lathes
2.Precisely depositing material-3D printer such as the RepRap & Makerbot
What is the use of cnc machines
What Does It Stand For
Engineers Love initial-isms, Mostly because they make saying long or complex phrases more efficient. In this case engineers coined the term CNC didn't feel like repeating computer Numeric Control Over and Over again.
How Does It Work?
If you breakdown the phrase you can glean the function of this technology. At Its Most basic a CNC machine manipulates an end effector in an established coordinate system to perform a task set about by the operator who controls it using a computer. CNC machines are typically used in an industrial setting; however, a printer is a good example of a nearly ubiquitous CNC machine.In order for a printer a deposit ink on a Piece of paper, it needs the instructions from an operator.The operator tells the computer what they want to print and the computer sends that information to the printer in a way the printer in a way the printer can understand. There is an unbroken thread from operator's thought to information on paper and this is the same as fabricating a part. The CNC machine allows the operator to talk through the computer to the mill, Lathe or printer to accomplish a task Quickly and with precision.
What Good Is It?
You can trace back a vast majority of the products you encounter to CNC machining. Whether they were made from CNC machines, prototypes on CNC machines, Or The tooling for making the product was made by a CNC machine, if It is a Physical product chances are very good CNC was involved.
It is an amazing technology. I got into a Little more detail here if you are interested.
Page Source: https://goo.gl/otdxVL
website: www.subauae.com
Post By: Irfan Khan
How To build a CNC Router
How to build a CNC Router
I have absolutely no idea where to begin. I want a Machine that can cut acrylics, G10, carbon fiber and if possible 200mm thick sheets of aluminmum.
What so I need to learn ?
What Stepping Motor, Router, Power Supply and table is good for this machine.
Where can I buy The parts?
What Stepping Motor, Router, Power Supply and table is good for this machine.
Where can I buy The parts?
Let,s Get Started
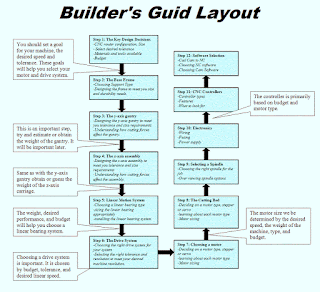
STEP 1: key Design Decisions
1.This section covers The Following
2.Identifying the right design for you
3.Required cutting area
4.Space availability
5.Materials
6.constructing Methods
7.Available tools
8.Budget
1.This section covers The Following
2.Identifying the right design for you
3.Required cutting area
4.Space availability
5.Materials
6.constructing Methods
7.Available tools
8.Budget
STEP 2 : The Base and X-axis Frame
This Section covers The following
1.Designing and Building main base or X-base
2.A breakdown of different designs
3.Fully Supported Frames
4.partially supported Frames Etc.
This Section covers The following
1.Designing and Building main base or X-base
2.A breakdown of different designs
3.Fully Supported Frames
4.partially supported Frames Etc.
STEP 3: The Y-Axis Gantry Design
This Section covers the following:
1.Designing and building the y-axis gantry
2.A breakdown of different designs
3.Forces and Moments on the Gantry
4.DO's and don't Etc.
This Section covers the following:
1.Designing and building the y-axis gantry
2.A breakdown of different designs
3.Forces and Moments on the Gantry
4.DO's and don't Etc.
STEP 4: The Z-Axis Assembly Design
This Section covers the following:
1.Designing and Building the Z-axis Assembly
2.Fores and Moments on the Z-axis Assembly
3.Linear rail/rods and bearing spacing
4.The Pluge arm Design Etc.
This Section covers the following:
1.Designing and Building the Z-axis Assembly
2.Fores and Moments on the Z-axis Assembly
3.Linear rail/rods and bearing spacing
4.The Pluge arm Design Etc.
STEP 5: The Linear Motion system
This section covers the following:
1.Detailed Overview of linear motion system
2.choosing the right system for your machine
3.Designing and building your own l
4.Linear Shaft and Bushings
Linear Rails and Guide Blocks Etc.
This section covers the following:
1.Detailed Overview of linear motion system
2.choosing the right system for your machine
3.Designing and building your own l
4.Linear Shaft and Bushings
Linear Rails and Guide Blocks Etc.
STEP 6: Machanical Drive Componets
This Section Cover the Following topics:
1.Detailed overview of the drive componets
2.chossing the right components for your design
3.Stepper and Servo motors
4.Lead screws and ball screws
5.Drive Nuts
6.Radial and thrust Bearings
7.Motor coupling and mouting
8.Direct drive vs. Geared
9.Rack and Pinions
10.Lead Screw motor sizing Etc..
This Section Cover the Following topics:
1.Detailed overview of the drive componets
2.chossing the right components for your design
3.Stepper and Servo motors
4.Lead screws and ball screws
5.Drive Nuts
6.Radial and thrust Bearings
7.Motor coupling and mouting
8.Direct drive vs. Geared
9.Rack and Pinions
10.Lead Screw motor sizing Etc..
STEP7:Choosing the Motors
This section covers the following topics:
1.Detailed overview of the CNC motors
2.Types of CNC motors
3.Stepper vs Servo motors
4.How stepper motors work & types of stepper motors
5.How servo motors work & types of servo motors
6.NEMA Standards
7.Choosing the right motor type for your design Motor Sizing Etc.
This section covers the following topics:
1.Detailed overview of the CNC motors
2.Types of CNC motors
3.Stepper vs Servo motors
4.How stepper motors work & types of stepper motors
5.How servo motors work & types of servo motors
6.NEMA Standards
7.Choosing the right motor type for your design Motor Sizing Etc.
STEP 8:The Cutting Table design
This Section covers the following:
1.The Cutting table design overview
2.T-slot Table
3.Vacuum Table
4.PerForated cutting Bed
5.The cutaway bed
6.Designing and Building your own Etc.
This Section covers the following:
1.The Cutting table design overview
2.T-slot Table
3.Vacuum Table
4.PerForated cutting Bed
5.The cutaway bed
6.Designing and Building your own Etc.
STEP 9: The Spindle Options
This Section Covers The Follwing:
1.CNC Spindle overview
2.Types and Features
3.Pricing and cost
4.Mouting and cooling options
5.Coolant systems
6.Building your own
7.How to calculate chip load and cutting force
8.How to fine optimal feed rates Etc.
This Section Covers The Follwing:
1.CNC Spindle overview
2.Types and Features
3.Pricing and cost
4.Mouting and cooling options
5.Coolant systems
6.Building your own
7.How to calculate chip load and cutting force
8.How to fine optimal feed rates Etc.
STEP 10: The Electronics
This Section covers the following:
1.CNC Eletronics overview
2.The Control Panel
3.Wiring and Fusing
4.Buttons and Switches
5.MPG's and Jog Wheels
6.Power Supplies Etc.
This Section covers the following:
1.CNC Eletronics overview
2.The Control Panel
3.Wiring and Fusing
4.Buttons and Switches
5.MPG's and Jog Wheels
6.Power Supplies Etc.
STEP 11: The CNC controller options
This section covers the following:
1.The CNC Controller overview
2.Controller Selection
3.Options available
4.Closed loop vs open loop systems
5.Best Prices controllers
6.Building your own from Scratch Etc.
This section covers the following:
1.The CNC Controller overview
2.Controller Selection
3.Options available
4.Closed loop vs open loop systems
5.Best Prices controllers
6.Building your own from Scratch Etc.
STEP 12:
This Section Covers the Following :
1.The CNC related Software overview
2.What software will I need
3.CAM software
4.CAD software
5.NC Controller Software
6.Best Choices free ware Etc.
This Section Covers the Following :
1.The CNC related Software overview
2.What software will I need
3.CAM software
4.CAD software
5.NC Controller Software
6.Best Choices free ware Etc.
Page source : https://goo.gl/stPikR
Website : www.subauae.com
Post By : Irfan khan
Thursday, October 22, 2015
Laser cutting Machine Technology
Laser cutting Machine Technology
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to cut materials, and is typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, but is also starting to be used by schools, small businesses, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser most commonly through optics. The laser optics and CNC (computer numerical control) are used to direct the material or the laser beam generated. A typical commercial laser for cutting materials would involve a motion control system to follow a CNC or G-code of the pattern to be cut onto the material. The focused laser beam is directed at the material, which then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas,[1] leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish. Industrial laser cutters are used to cut flat-sheet material as well as structural and piping materials.
In 1965, the first production laser cutting machine was used to drill holes in diamond dies. This machine was made by the Western Electric Engineering Research Center.[2] In 1967, the British pioneered laser-assisted oxygen jet cutting for metals.[3] In the early 1970s, this technology was put into production to cut titanium for aerospace applications. At the same time CO2 lasers were adapted to cut non-metals, such as textiles, because, at the time, CO2 lasers were not powerful enough to overcome the thermal conductivity of metals
Power Consumption
The main disadvantage of laser cutting is the high power consumption. Industrial laser efficiency may range from 5% to 45%.[13] The power consumption and efficiency of any particular laser will vary depending on output power and operating parameters. This will depend on type of laser and how well the laser is matched to the work at hand. The amount of laser cutting power required, known as heat input, for a particular job depends on the material type, thickness, process (reactive/inert) used, and desired cutting rate.
Amount of heat input required for various material at various thicknesses using a CO2 laser [watts]
| Production and cutting rates | ||||||
The maximum cutting rate (production rate) is limited by a number of factors including laser power, material thickness, process type (reactive or inert,) and material properties.
Common industrial systems (≥1 kW) will cut carbon steel metal from 0.51 – 13 mm in thickness. For all intents and purposes, a laser can be up to thirty times faster than standard sawing.
cutting rates for various materials and thincknesses using a co2 laser [cm/second]
Cutting rates for various materials and thicknesses using a CO2 laser
| Workpiece material | Material thickness | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.51 mm | 1.0 mm | 2.0 mm | 3.2 mm | 6.4 mm | 13 mm | |
| Stainless steel | 42.3 | 23.28 | 13.76 | 7.83 | 3.4 | 0.76 |
| Aluminium | 33.87 | 14.82 | 6.35 | 4.23 | 1.69 | 1.27 |
| Mild steel | − | 8.89 | 7.83 | 6.35 | 4.23 | 2.1 |
| Titanium | 12.7 | 12.7 | 4.23 | 3.4 | 2.5 | 1.7 |
| Plywood | − | - | − | - | 7.62 | 1.9 |
| Boron / epoxy | − | - | − | 2.5 | 2.5 | 1.1 |
Page Source : https://goo.gl/YbVHgw
website : www.subauae.com
Post by : Irfan khan
Wednesday, October 21, 2015
CNC Router Machine
CNC Router Machine
A CNC router is a computer controlled cutting machine related to the hand held router used for cutting various hard materials, such as wood, composites, aluminium, Steel, plastics, and foams. CNC stands for computer numerical control. CNC routers can perform the tasks of many carpentry shop machines such as the panel saw, the spindle Mulder, and the boring machine. They also cut mortises and tenons.
A CNC router is a computer controlled cutting machine related to the hand held router used for cutting various hard materials, such as wood, composites, aluminium, Steel, plastics, and foams. CNC stands for computer numerical control. CNC routers can perform the tasks of many carpentry shop machines such as the panel saw, the spindle Mulder, and the boring machine. They also cut mortises and tenons.
 |
| Drawing of Table Top Diy CNC Router, Silver: Iron Red: Stepper Motors , light Brown MDF, Dark Brown: Hard Wood. |
A CNC router is very similar in concepts to a CNC milling machine. instead of routing by hand, tool paths are controlled via computer numerical control. The CNC router is one of many kinds of tools that have CNC variants
 |
| Cnc Router Machines |
A CNC router typically produces consistent and high-quality work and improves factory productivity. unlike a Jig router, the CNC router can produce a one-off as effectively as repeated identical production. Automation and precision are the key benefits of cnc router tables
A CNC router can reduce waste, frequency of errors, and the time the finished product takes to get to market
Applications
A CNC router can be used in the production of many different items, such as door carvings, interior and exterior decorations wood panels, sign boards, wooden frames, moldings, musical instruments, furniture, and so on. in addition, the CNC router helps in the Thermos forming of plastics by automating the trimming process. CNC router can help ensure part repeat ability and sufficient factory output.
Overview of CAM (computer-aided manufacturing)
CAM software makes the CAD drawing/design into a code called g-code. This code the cnc machine can understand. in short, CNC technology is not very complicated. it is a tool controlled by a computer. it only becomes more sophisticated when considering how the computer controls the tool. The illustration shows what a bare bones CNC machine might look like without its controller.
Sizes and configurations of router
CNC routers come in many configurations, from small home-style D.I.Y. "desktop" like K2 cnc, to large industrial CNC routers used in sign shops, cabinet making, aerospace and boat-making facilities. Although there are many configuration, most CNC router have a few specific parts: a dedicated CNC controller, one or more spindle motors, servo motors, stepper Motors, Servo amplifiers, AC Invert-er drives, linear guides, ball nuts and a work space table or tables. in addition, CNC router may have vacuum pumps, with grid table tops or t slot hold down fixtures to hold the parts in place for cutting. CNC routers are generally available in 3-axis and 5-axis CNC formats. Many Manufacturers offer A and B Axis for full 5 Axis capabilities.
Controlling the machine
The CNC router is controlled by a computer. co-ordinates are uploaded into the machine controller from a separate CAD program. CNC router owners often have two Software applications-one program to make designs (CAD) and another to translate those designs into a 'G-code' program of instructions for the machine (CAM). As with CNC Milling machines, CNC router can be controlled directly byy manual programming, and CAD/CAM opens up wider possibilities for contouring, speeding up the programming process and in some cases creating programs whose manual programming would be, if not truly impossible, certainly commercially impractical.
Types
Wood
Main article : CNC wood router
A CNC wood router is a CNC Router tool that Creates objects from wood. CNC stands for computer numerical control. The CNC works on the Cartesian coordinate System (X,Y,Z) for 3D motion control. parts of a project can be designed in the computer with a CAD/CAM program, and then cut automatically using a router or other cutters to produce a finished part.The CNC Router is ideal for Hobbies, engineering prototyping, product development, art and production work.
Metal
Main article : Milling Machine
Milling is the machining process of using rotary cutters to remove material from a workpiece advancing (or feeding ) in a direction at an angle with the axis of the tool It covers a wide variety of different operations and machines, on scales from small individual parts to large, heavy-duty gang milling operations it is one of the most commonly used processes in industry and machine shops today for machining parts to precise sizes and shapes.
Page Source:https://goo.gl/lSt3VE
website:www.subauae.com
Post by : Irfan Khan
Tuesday, October 20, 2015
How many type of Cnc Machine
 |
| CNC Machine & laser Machine. |
As many as your heart Desires; if your production process needs a degree of motion (or other control ) and you can put a computer-controlled sensor and actuator on it, you have a CNC machine.
Five and six-axis machines can really blur the traditional distinctions between "lathes" and "horizontal mills", but That's all the better for production Flexibility.
There are basically five different types of CNC machines:
1.CNC Plasma Cutting Machine
2.CNC laser Cutting Machine
3.CNC Milling Machine
4.CNC Router Machine
5.CNC Lathe Machine
3.CNC Milling Machine
4.CNC Router Machine
5.CNC Lathe Machine
All the Five Types of machines have their own applications in a verity of industries. Let's find out which types of industries are using such machines and what the application of each of the machine is.
when CNC was first invented it was a technology that was adapted to fit existing tools but there are also many machines which are created for the sole purpose of being CNC machines.
when CNC was first invented it was a technology that was adapted to fit existing tools but there are also many machines which are created for the sole purpose of being CNC machines.
Milling Machine
Milling machines are often retrofitted with CNC technology. This process involves removing all the mechanisms built into the machine to make it easy for a human to operate, Such as Hand Wheels and DRO (Digital Read Out) electronics.
The machine will usually have its old lead screws replaced with new very high accuracy ball screws and various new mounts built for mounting the actuators to the machine.
Lathe
just like the milling machine, lathes are also commonly retrofitted with CNC technology in the exact same way.
Machines that are Custom Built For CNC operation
Router
CNC Router are a very common piece of machinery you will see a lot when learning about CNC. These are machines built exclusively to be operated by CNC technology and have no human interface other than through the computer.
Routers are generally for producing larger work and more commonly built with the idea of cutting wood, plastics and sheet metal in mind. Router also are most commonly found in a 3 axis setup (X,Y and Z.) Thiz set up will allow cutting of basic profiles and 3 dimensional relief machining. there are also CNC router which are 4, 5 or even 6 axis, these machines are more suited towards cutting more complex shapes or prototype models.
Milling machine
There are many milling machines today which were built specifically for CNC as opposed to being retrofitted at a later stage.Some of these machines can be absolutely massive and have built in tool changers, auto-feed mechanisms for loading in material and various electrical sensors for safe monitored cutting.
CNC plasma Cutter
CNC plasma cutters are very similar to CNC routers in size and setup, however plasma cutters don't require as much of a powerful set because as opposed to dragging around a spinning tool in material they fly above the table with a plasma torch.plasma cutter are made for cutting 2 dimensional profile shapes into sheet metal.
Cnc laser cutter
CNC laser cutters follow the same principle as the plasma cutter. However laser cutter use a much less destructive force than a plasma torch-A laser. laser cutters are often good for cutting wood, plastic and metal. Each will need a different strength of laser suited for the material.
3D printer
A 3D printer or 3 Dimensional printer uses a similar set up as a CNC router or laser cutter, except it uses a plastic extrudes. This plastic extrude pushes out hot plastic through a tiny hole and slowly, by layer deposits enough plastic to build up a completed part.
Pick and place Machine
A pick and place machine again uses a similar set up as a cnc router or laser cutter. This time there a multiple small nozzles, that pick up electrical component down. hence the name pick and place.
pick and place machines move very quickly and are used to palace the many hundreds or thousands of electrical components that make up Services such as computer motherboards, phones/tables, and pretty much everything else that has a printed circuit board.
pick and place machines move very quickly and are used to palace the many hundreds or thousands of electrical components that make up Services such as computer motherboards, phones/tables, and pretty much everything else that has a printed circuit board.
Many types of CNC machines exists out if which very few are know such as
1.Retrofitted Machine which includes machines like Milling Machines, Lathe Machines Etc. Which uses rectification with CNC Technology.
2. Custom Built Machines For CNC operation: it includes machines like Routers, Milling Machines, CNC Plasma Cutter, 3D printer, Pcik and Place Machines Etc.
If a tool exists you can Probably run it with CNC.
1.Lathes 2. Mills 3.Router 4.grinders 5.welder 6.Torch & plasma cutters 7.Water Jet 8.laser 9. Plotters/paper cutters 10.measuring 11. 3 D printers
There are Probably some cake decoration a Machine
Page Source: https://goo.gl/J86Yn5
Website: www.subauae.com
Post by : Irfan Khan
Sunday, October 18, 2015
Suba Tech Trading LLC
Young inventors in the state will get a helping hand to realize their creative dreams with mini fab labs in engineering colleges
Engineering students can now let their imaginations run wild. coming to select which help convert those imaginative ideas to prototypes. the ambitious venture is being rolled out under the aegis of kerala technological university (KTU), in association with the Kerala startup Mission (KSM).
"Twenty collages will have mini fab labs in the initial phase of the project. We had received 46 application from the affiliated engineering colleges. An expert committee will short-list the frist 20," said M.Addul Rahman, Pro-Vice Chancellor of KTU.
Jayasankar Prasad C., Chief Executive officer of KSM, Pointed out that the aim of the initiative is to bring a marker ecosystem in the state. "It will usher an in-house development facility in educational institutions and mould talents with skills in design, development and fabrication," He said.
the Project Proposal said that the min i Fab lab will work on a partnership model, where KSM and rhe host institution and mould talent with skills the cost on a 50:50 basis.
Experts representing Fab Lab Kerala (comprising the two Fab Labs in Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram set up by the goverrnment with the support of Massachusette Institute of Technology) will Provide the technical expertise to run and maintain the mini fab labs. the partnering institution wll buy the equipment. KSM will undertake the installation of the labs under the supervision of technical experts from the fab foundation.
some of the equipment in a mini lab includes laser cutter-mini version; mill/router cnc; Vinyl cutter; electronics workbench: function generator; soldering station and accessories. other consumables and accessories for each equipment include softwood, acrylic boards, copper clads, wax vinyl, copper tapes eletronics workbench Kit and cleaning tools
people behind the initiative exuded confidence while started that the proposed mini fab labs will help in stepping up the technical skills of both students and teachers. they will also get wide recognition as Fab Lab course and certification are accepted globally. young inventors have an opportunity to get international visibility for their product besides getting a chance to collaborate on Fab Lab Projects Through the Fab Lab network. The youngsters could Explore the advantage of having dedicated channel to connect with fab gurus at fab labs in Kochi and Thiruvananthapuram.
They will also Receive opportunities to collaborate with kerala startup Mission to develop startups based on products developed at the mini Fab Labs.
Page Source: http://goo.gl/RQEaYF
website : www.subauae.com
Post by : Irfan Khan
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)